- About Us
-
Wire Mesh
- Welded Wire Mesh RollsChain Link FenceChicken Wire NettingHolland Wire MeshWelded Wire Mesh PanelBlack Woven Wire MeshCrimped Wire MeshStainless Steel Wire MeshMetal Conveyor BeltsGalvanized Wire MeshWire BasketPlastic MeshSurgical Instrument BasketSoap CageWindow Screen CustomCustom Fiberglass Window ScreenFiberglass MeshShade-NetConstruction Safety NetStainless Steel Security MeshAluminum Wire MeshWire Rope MeshConcrete Reinforcing MeshHigh Rib Formwork MeshRib LathGalvanized Chain Link Wire MeshGalvanized Cyclone FenceGalvanized Square Wire MeshHot-Dipped Galvanized Wire MeshPVC Chain Link Wire MeshPvc Coated Chain Link Fence
- Wire and Nails
- Filters
-
Special Alloy Wire Mesh
- Dutch Weave Stainless Steel Wire MeshReverse Dutch Weave Stainless Steel Wire MeshThe Duplex Stainless Steel Wire Mesh UNS 2304Duplex Stainless Steel Wire Mesh UNS S31803(S32205)Super Duplex Stainless Steel Wire Mesh UNS 32750Plain or Twill Weaved Stainless Steel Wire MeshBrass Wire MeshCopper Wire MeshPhosphor Bronze Wire MeshFeCrAl Wire MeshPure Nickel Wire MeshMonel Wire MeshInconel Wire MeshNichrome Wire MeshHastelloy Wire MeshSilver Wire MeshTitanium Wire MeshTungsten Wire MeshMolybdenum Wire Mesh
- Decorative Mesh
-
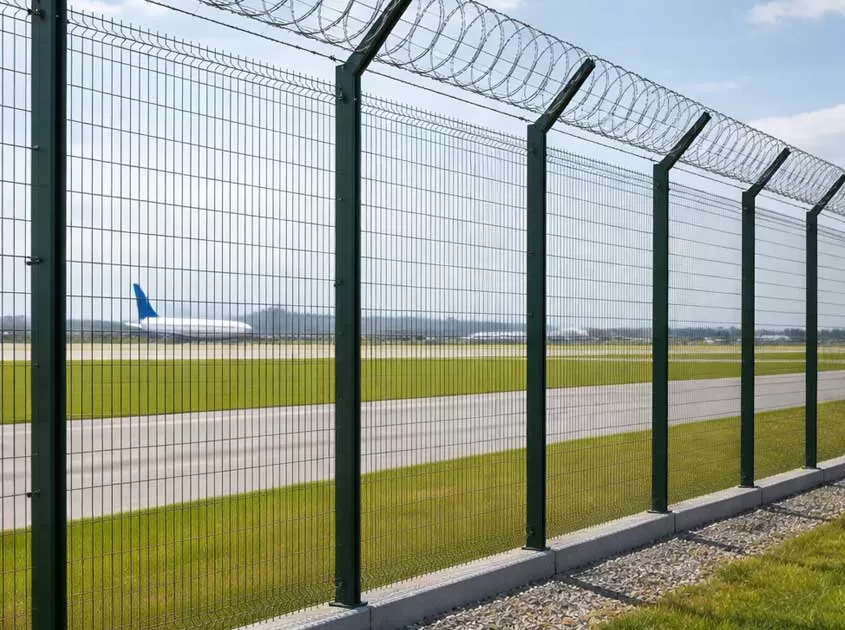
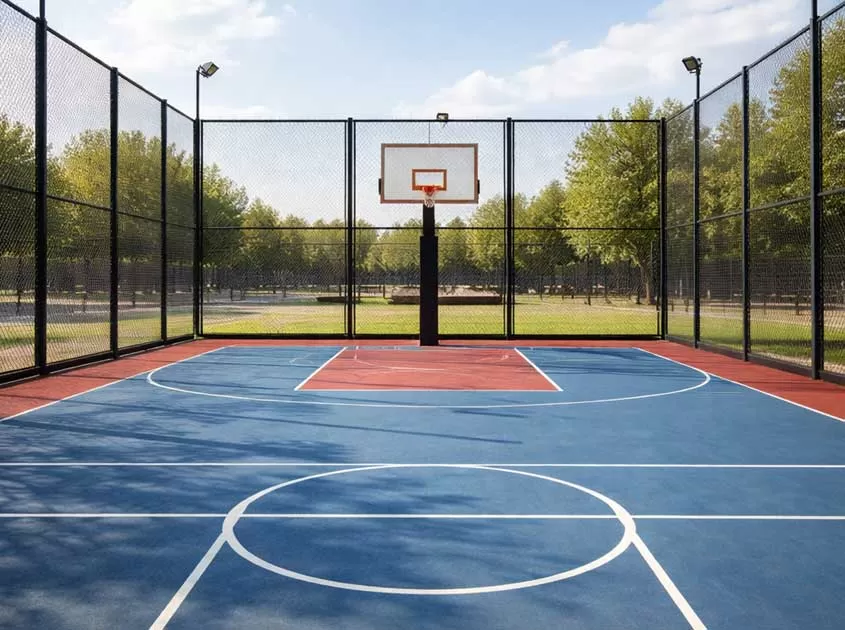
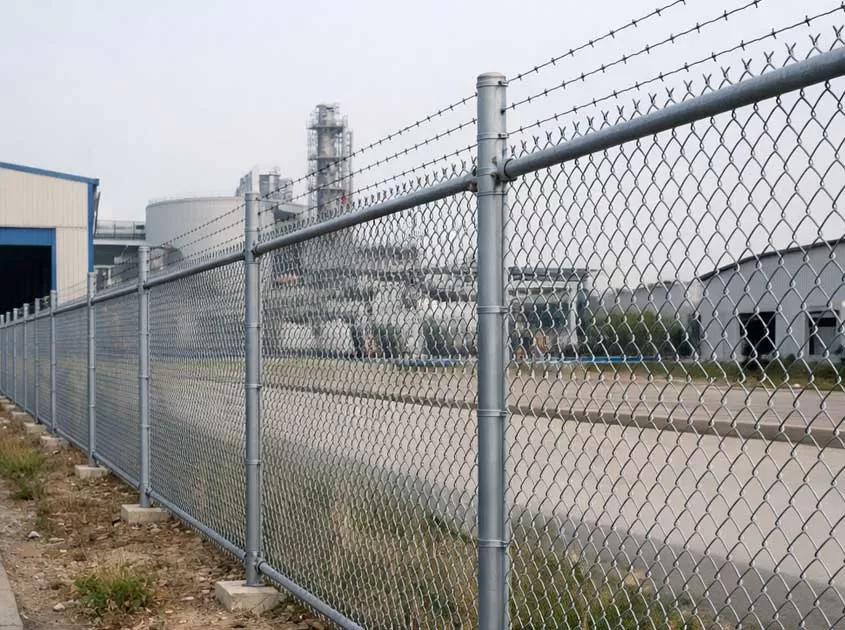
Fencing
- Welded Wire Mesh FenceDouble Wire FencingChain Link Fence358 Fence.High security fencingSteel Picket FenceFarm Fence & Field FenceBRC fencing . Roll Top FencePalisade FenceCanada Temporary FenceAustralia Temporary FenceAirport FenceConcertina Razor WireGabion BasketMetal steel garden bedWelded Gabion
-
Cages and Equipments
- Chick Chicken CagesRabbit CagesBroiler Chicken CagesLayer Chicken CagesQuail CagesAccessories for chicken cageAutomatic Feeding SystemSemi-automatic poultry feeding equipmentAutomatic Manure Cleaning SystemAutomatic egg collection systemVertical feed mill and mixerEgg IncubatorPlucker MachineEgg sorter egg grading machineBrooder HeaterDebeaking MachineExhaust fanManure Dewatering MachinePlate Mould Pellet MachinePlasson Drinker&Bell DrinkerFeed Storage Farm SiloEvaporative Cooling Pads
- Expanded and Perforated
- Contact