About chain link fence-hot and cold galvanizing process
Explain the difference of hot-dip galvanizing process of hook net! The hook net is the inner net of the slope protection net. Whether it is an active slope protection net or a passive slope protection net, the hook net is required as the inner net. Because the outer net of the slope protection net is relatively large, it is mainly used to carry larger stones. Mainly bear the impact of smaller stones. Galvanized chain link fence mainly adopts the special effect of air permeability of chain link fence, which is widely used in mountain protection, used to fix rocks, and sprayed with green grass seeds to achieve the effect of self-curing in the later stage.

Cold galvanizing is a physical treatment, just brushing a layer of zinc on the surface, so the zinc layer is easy to fall off. Hot-dip galvanizing is often used in building construction. Continuous hot-dip galvanizing process: steel→heating→cooling to galvanizing temperature→galvanizing→cooling. Cold galvanizing, also known as electro-galvanizing, is only 10-50g/m2, and its corrosion resistance is much different than that of hot-dip galvanizing. The price of electro-galvanized chain link fence is relatively cheaper. Hot-dip galvanizing means that the steel body is galvanized on the surface under the condition of hot dipping. It has strong adhesion and is not easy to fall off. Although the hot-dip galvanized pipe also appears rust, it can meet the requirements of technology and hygiene in a long period of time. Claim.
First of all, the difference of hot-dip galvanizing is that after degreasing, pickling, dipping, drying, soaking in the dissolved zinc solution, and then lifting. Cold galvanizing, also known as galvanizing, refers to the use of electrolysis equipment to remove oil, pickling into the zinc salt solution, and connect the negative electrode of the electrolysis equipment; connect the zinc plate to the positive electrode of the electrolysis equipment relative to the workpiece, turn on the power, and use The current moves from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, depositing the zinc layer on the workpiece.
-
 Best Welded Wire Mesh for South American Markets Feb 03, 2026
Best Welded Wire Mesh for South American Markets Feb 03, 2026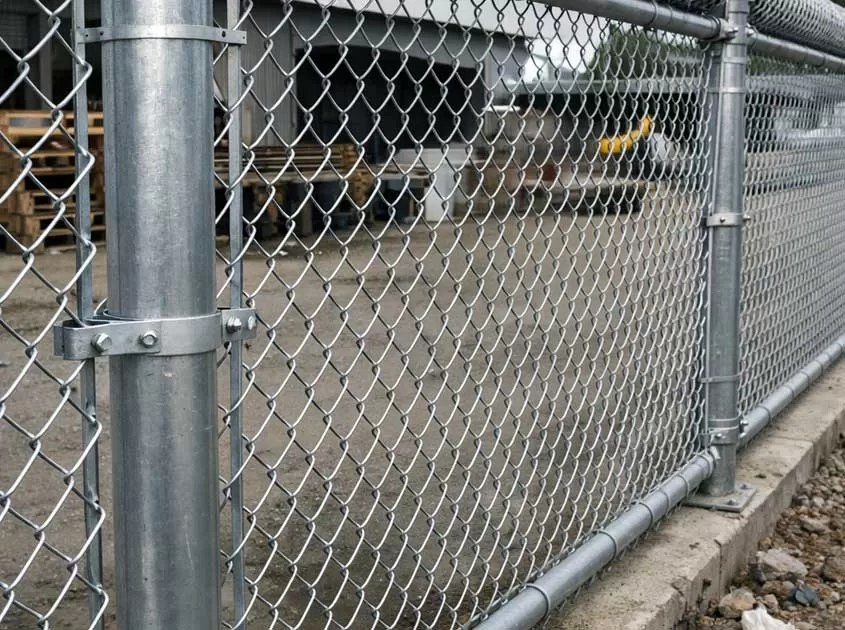 Why Galvanized Wire Mesh Is Popular in South America Jan 26, 2026
Why Galvanized Wire Mesh Is Popular in South America Jan 26, 2026 How to Check the Quality of Welded Wire Mesh Jan 16, 2026
How to Check the Quality of Welded Wire Mesh Jan 16, 2026
- Tel.: +86 311 83077076
- E-mail: sales@qunkunmetal.com
- Skype: qunkunsales01
- WhatsApp: 8618032412189
- Add.: No.69 The Filter Industrial Part of Anping, Hebei, China


















