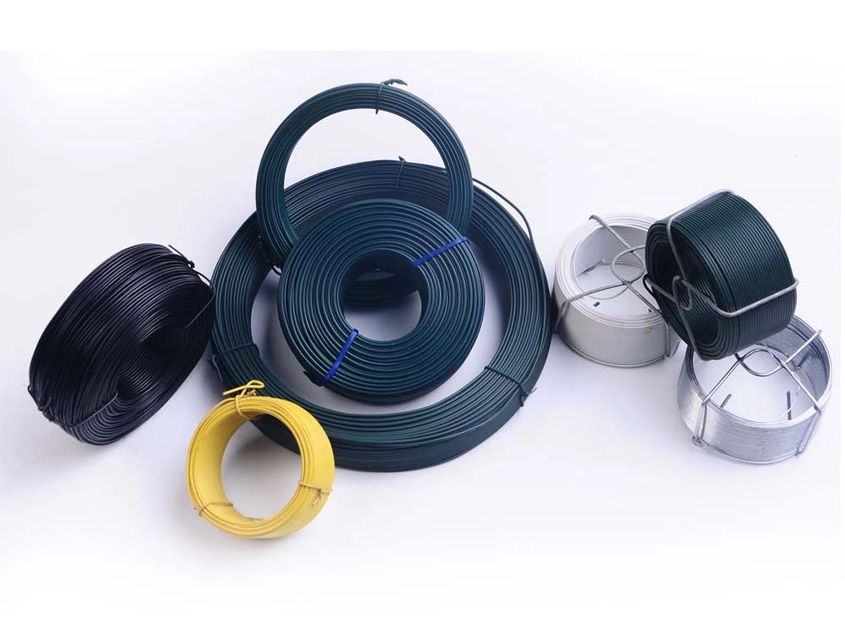
Types and Characteristics of Iron Wire
Iron wire is a versatile material widely used across various industries, including construction, agriculture, automotive, and manufacturing. Its properties can be tailored through different processing techniques, making it suitable for a range of applications. Below is an overview of the primary types of iron wire and their characteristics.
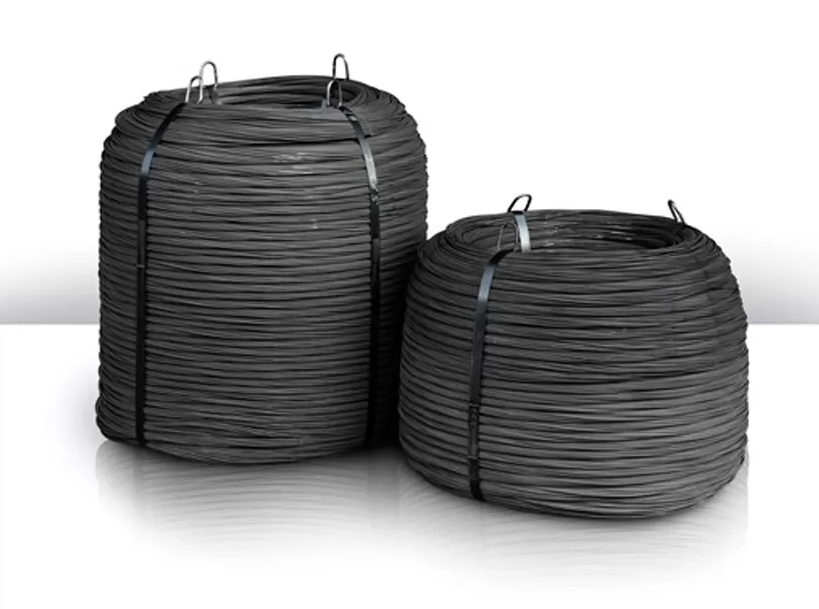
1. Black Iron Wire
Characteristics of Black Iron Wire:
Material: Made from low-carbon steel that has not undergone any surface treatment.
Surface: Features a matte black finish due to the absence of coating.
Strength: Black Iron Wire offers moderate tensile strength and flexibility.
Applications of Black Iron Wire:
Commonly used in general-purpose applications such as fencing, binding, and crafting.
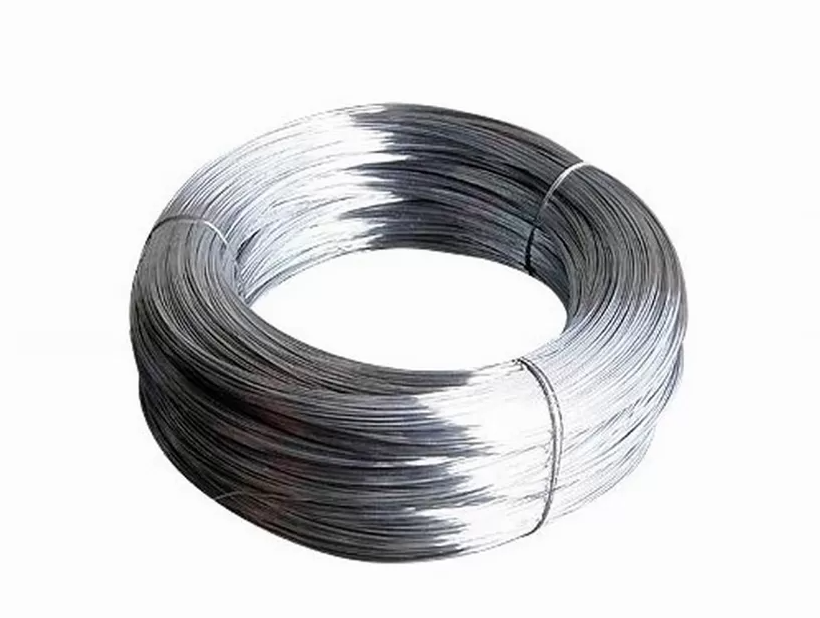
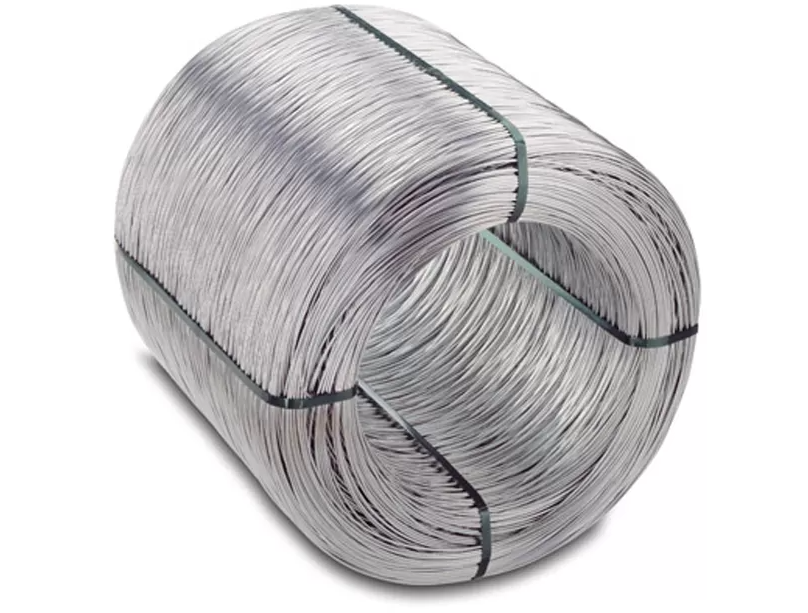
2. Galvanized Iron Wire
Types of Galvanized Iron Wire:
Electro-Galvanized Wire: Coated with a thin layer of zinc through electroplating.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Wire: Dipped into molten zinc to form a thicker, more durable coating.
Characteristics Galvanized Iron Wire:
Corrosion Resistance: The zinc coating provides excellent protection against rust and corrosion.
Durability: Hot-dip galvanized wire offers superior longevity compared to electro-galvanized wire.
Appearance: Hot-dip galvanized wire has a matte finish, while electro-galvanized wire appears shinier.
Applications Galvanized Iron Wire:
Used in construction for reinforcing concrete, in agriculture for fencing, and in manufacturing for wire mesh production.
3. Annealed Iron Wire
Characteristics of Annealed Iron Wire:
Material: Low-carbon steel wire that has been heat-treated to increase ductility.
Flexibility: Highly flexible and easy to bend without breaking.
Surface: Smooth finish, often black or slightly shiny.
Applications of Annealed Iron Wire:
Ideal for binding, tying, and weaving applications due to its pliability.
4. Stainless Steel Wire
Characteristics of Stainless Steel Wire:
Material: Composed of iron, chromium, and sometimes nickel, offering enhanced corrosion resistance.
Strength: Exhibits high tensile strength and resistance to wear.
Appearance: Shiny, metallic finish.
Applications of Stainless Steel Wire:
Widely used in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals, such as in marine applications, medical devices, and food processing equipment.
5. High Carbon Steel Wire
Characteristics of High Carbon Steel Wire:
Material: Contains a higher percentage of carbon, resulting in increased hardness and strength.
Brittleness: More brittle compared to low-carbon steel wires.
Surface: May have a shiny or matte finish depending on processing.
Applications of High Carbon Steel Wire:
Suitable for applications requiring high strength, such as in the production of springs, piano wires, and cutting tools.
6. Alloy Steel Wire
Characteristics of Alloy Steel Wire:
Material: Steel alloyed with elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum to enhance specific properties.
Properties: Improved resistance to heat, wear, and corrosion.
Surface: Varies based on alloy composition and treatment.
Applications of Alloy Steel Wire:
Utilized in demanding applications such as automotive components, industrial machinery, and structural reinforcements.
7. FeCrAl (Iron-Chromium-Aluminum) Alloy Wire
Characteristics of FeCrAl (Iron-Chromium-Aluminum) Alloy Wire:
Composition: An alloy of iron, chromium, and aluminum.
High-Temperature Resistance: Can withstand temperatures up to 1500°C.
Oxidation Resistance: Forms a protective aluminum oxide layer when heated, enhancing durability.
Applications of FeCrAl (Iron-Chromium-Aluminum) Alloy Wire:
Commonly used in heating elements, industrial furnaces, and other high-temperature applications.
8. Electrical Steel Wire
Characteristics of Electrical Steel Wire:
Material: Iron alloyed with silicon to improve magnetic properties.
Magnetic Permeability: High relative permeability, reducing energy loss in electromagnetic applications.
Heat Treatment: Processed to enhance magnetic properties and reduce hysteresis loss.
Applications of Electrical Steel Wire:
Essential in the manufacturing of transformers, electric motors, and generators.
Conclusion
Iron wire comes in various types, each with distinct characteristics tailored to specific applications. Whether it's the flexibility of annealed wire, the corrosion resistance of galvanized wire, or the high-strength properties of high carbon steel wire, selecting the appropriate type ensures optimal performance in its intended use. Understanding these differences is crucial for industries ranging from construction to electronics, as it directly impacts the durability, efficiency, and safety of the final product.
-
 Why Galvanized Wire Mesh Is Popular in South America Jan 26, 2026
Why Galvanized Wire Mesh Is Popular in South America Jan 26, 2026 How to Check the Quality of Welded Wire Mesh Jan 16, 2026
How to Check the Quality of Welded Wire Mesh Jan 16, 2026
- Tel.: +86 311 83077076
- E-mail: sales@qunkunmetal.com
- Skype: qunkunsales01
- WhatsApp: 8618032412189
- Add.: No.69 The Filter Industrial Part of Anping, Hebei, China

























